Research
Research Focus
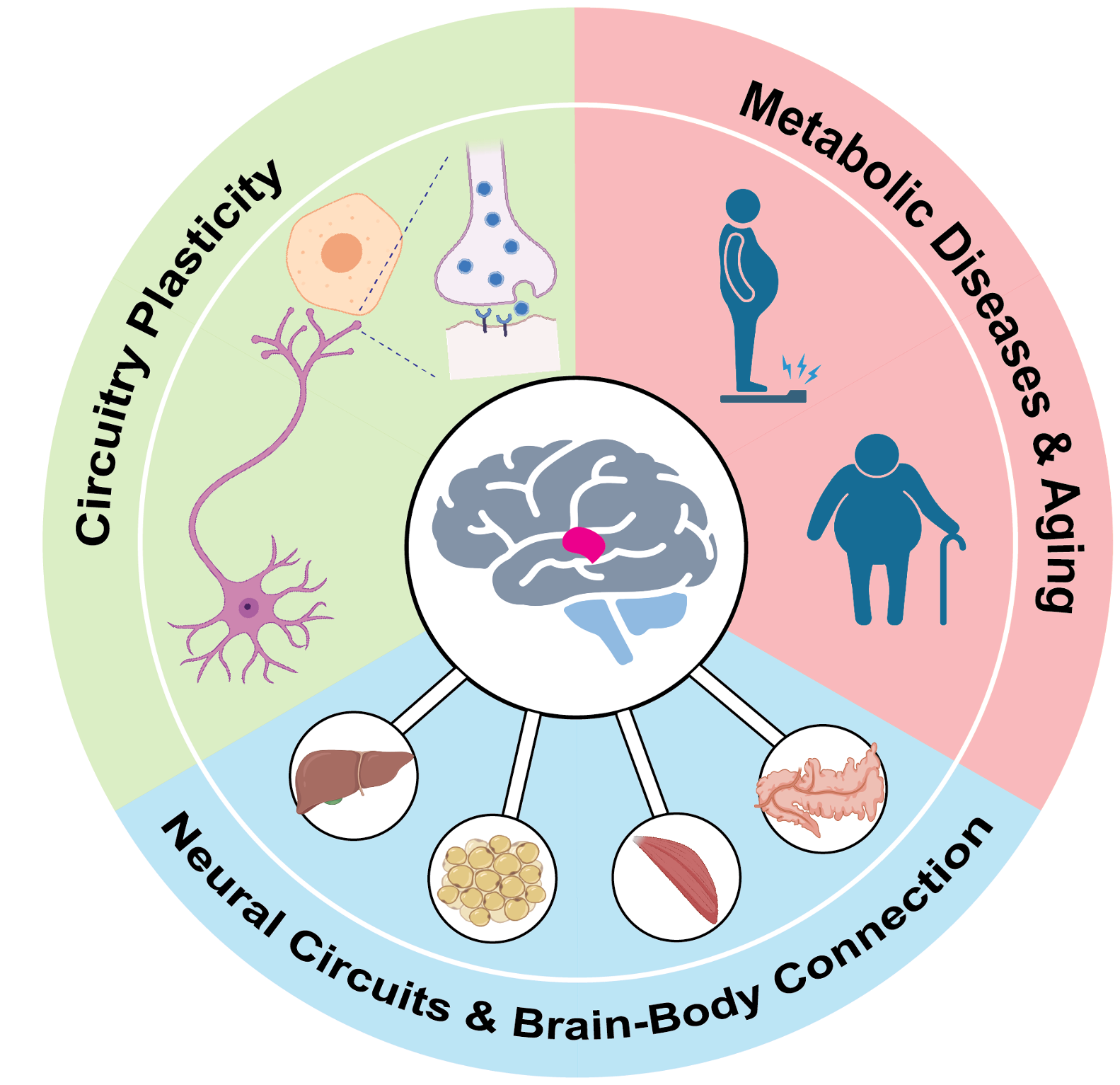
The brain plays a central role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis and aging, and it is a significant contributor to metabolic diseases such as obesity and diabetes, as well as many age-related disorders. Targeting specific brain regions or cell types has shown great promise for improving metabolic health and aging, though the underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. Our overarching goal is to map the genes, cells, and neural circuits that regulate metabolic homeostasis and the aging process, while also uncovering the mechanisms that drive metabolic diseases and their impact on aging. To address this, we focus on three key areas:.
1. Sensing and Function
How does the brain detect and interpret metabolic signals, and how are these signals translated into regulatory functions? Using unbiased approaches such as whole-brain activity mapping and single-cell multiomics, we aim to identify key cell types that are critical for the regulation of specific metabolic processes.
2. Adaptation and Homeostasis
How do neurons communicate with other neurons and peripheral organs to maintain homeostasis, and how does this communication change with aging? We investigate the molecular mechanisms of neuron–neuron and neuron–organ interactions, as well as the plasticity of these circuits across metabolic states and aging conditions.
3. Diseases and Therapy
What goes wrong in metabolic diseases and aging, and can targeting these changes provide new treatments? By dissecting the molecular mechanisms underlying obesity, diabetes, and age-related decline, we seek to identify precise therapeutic targets to restore metabolic health and promote healthy aging.